回答这个问题,我们需要掌握MyBatis的缓存概念,如果我们两次查询,一次是数据库查询,而第二次直接取得缓存中的数据,那么这两次查询查询的数据就是同一个对象
Mybatis的一级缓存是Session级别的缓存。一级缓存的作用域默认是一个SqlSession。Mybatis默认开启一级缓存。
在同一个SqlSession中,执行相同的查询SQL,第一次会去数据库进行查询,并把对象放入缓存中,第二次以后是直接去缓存中取。
当执行SQL查询中间发生了事务提交(增删改都会触发自动提交)的操作,都会把当前SqlSession的缓存清空。
只要两条SQL的下列五个值相同,即可以认为是相同的SQL。
Statement Id + Offset + Limmit + Sql + Params
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
//MappedStatement的id
// id 就是Sql语句的所在位置 包名 + 类名 + SQL名称
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
// offset 就是 0
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
// limit 就是 Integer.MAXVALUE
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
// 具体的SQL语句
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
//后面是update了sql中带的参数
cacheKey.update(value);
...
下面我以例子说明:
一级缓存开启
Demo1:
@Test
public void testLocalCache() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(true);
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//第一次经过数据库查询
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// 同一个sqlSession,走缓存
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession.close();
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
我们发现,当我们开启一级缓存,同一个sql查询只有第一次经过了数据库,后面两次都走了缓存
Demo2:
@Test
public void testLocalCacheClear() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession(true); // true为自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// 自动提交事务,清空了缓存
System.out.println("增加了" + studentMapper.addStudent(buildStudent()) + "个学生");
// 缓存为空,重新查询数据库
System.out.println(studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession.close();
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: INSERT INTO student(name,age) VALUES(?, ?)
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 明明(String), 20(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
增加了1个学生
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
提交事务会把缓存清空
Demo3
@Test
public void testLocalCacheScope() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // true为自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true);
// 两个不同的sqlSession
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 第一次从数据库中读
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// 一个session,从一级缓存中读
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// 清空sqlSession2的一级缓存
System.out.println("studentMapper2更新了" + studentMapper2.updateStudentName("小岑",1) + "个学生的数据");
// sqlSession1的一级缓存还在
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// sqlSession2一级缓存没了,所以重新从数据库读
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
执行结果:
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: UPDATE student SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 小岑(String), 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
studentMapper2更新了1个学生的数据
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
一级缓存只会影响一个session,不同的session互不影响
mybatis中的二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存。
二级缓存开启后,同一个namespace下的所有操作语句,都影响着同一个Cache,即二级缓存被多个SqlSession共享。
当开启缓存后,数据的查询执行的流程就是 二级缓存 -> 一级缓存 -> 数据库。
需要注意的是,只有当事务提交或者Session关闭之后,才会把查到的数据放到二级缓存中
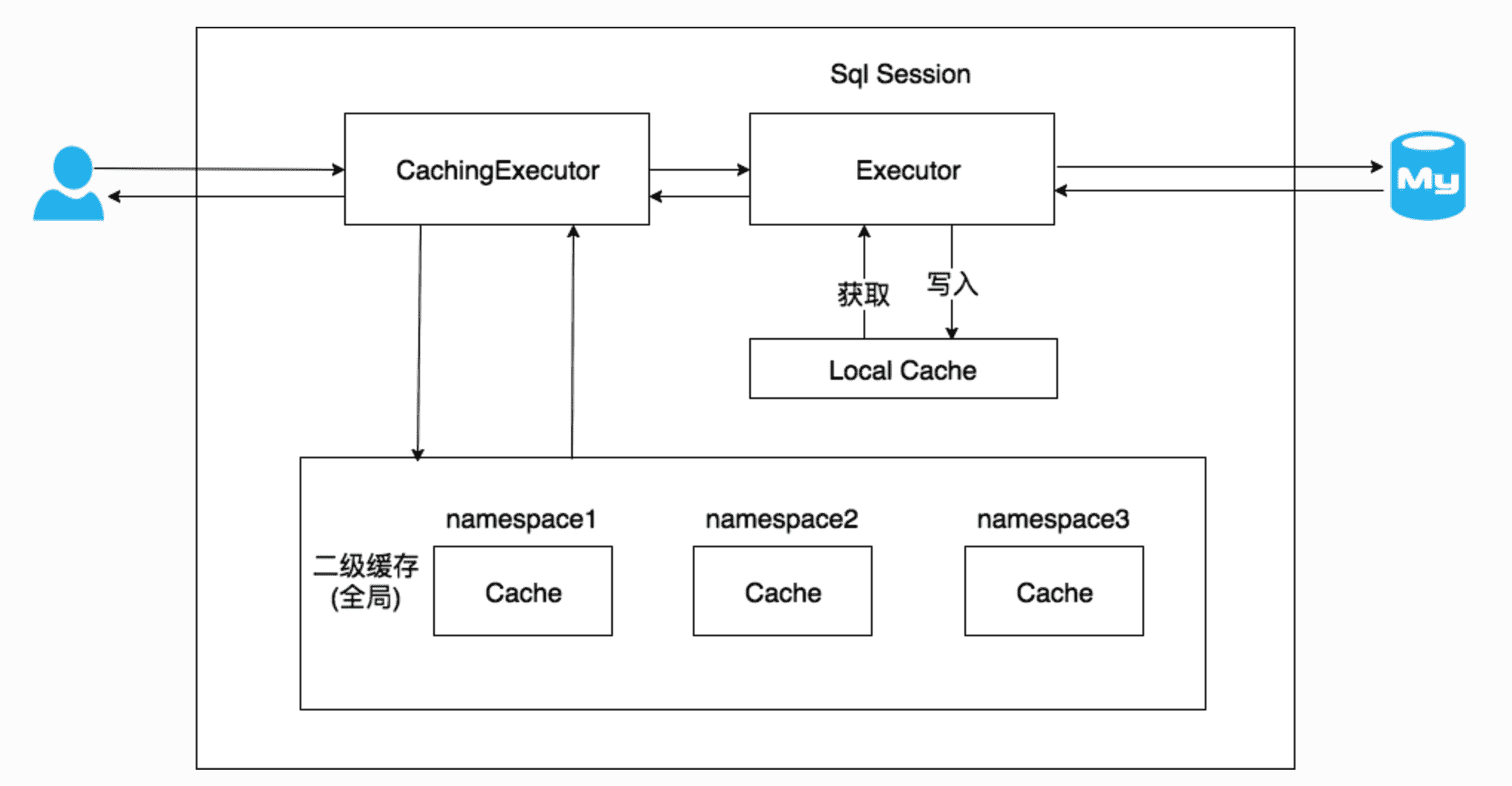
我们可以在mapper.xml中添加来启用二级缓存
二级缓存的执行原理和前面提到的一级缓存是差不多的,二级缓存与一级缓存区别在于二级缓存的范围更大,多个sqlSession可以共享一个mapper中的二级缓存区域。
下面我以例子说明:
一级、二级缓存开启
Demo1
@Test
public void testCacheWithoutCommitOrClose() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // true为自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true);
// 两个不同的sqlSession
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// Mapper的nameSpace相同,不管是不是同一个session,都可以用二级缓存
// 但是因为sqlSession1未提交,所以没有存入二级缓存。
// 只能从数据库查出
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
session未提交的话,是不会放入二级缓存的
Demo2
@Test
public void testCacheWithCommitOrClose() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // true为自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true);
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
// sqlSession1关闭或事务提交,则放入二级缓存
sqlSession1.close();
// 从二级缓存中取出
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 小岑, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.5
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='小岑', age=16, className='null'}
同一个nameSpace,session1提交后,可从二级缓存查出
Demo3
@Test
public void testCacheWithUpdate() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true);
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true);
SqlSession sqlSession3 = factory.openSession(true);
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper3 = sqlSession3.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentById(1));
sqlSession1.close();
// sqlSession1关闭后,可从二级缓存中查出
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
studentMapper3.updateStudentName("方方",1);
// 提交会清空二级缓存
sqlSession3.commit();
// 从数据库查
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentById(1));
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 方方, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.5
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='null'}
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: UPDATE student SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 方方(String), 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.3333333333333333
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT id,name,age FROM student WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 方方, 16
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='null'}
Demo4
@Test
public void testCacheWithDiffererntNamespace() throws Exception {
SqlSession sqlSession1 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession2 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession3 = factory.openSession(true); // 自动提交事务
StudentMapper studentMapper = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
StudentMapper studentMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
ClassMapper classMapper = sqlSession3.getMapper(ClassMapper.class);
System.out.println("studentMapper读取数据: " + studentMapper.getStudentByIdWithClassInfo(1));
sqlSession1.close();
// 可从二级缓存中查出
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentByIdWithClassInfo(1));
// 提交只清空了classMapper的二级缓存,没有清空StudentMapper的二级缓存,所以读到了脏值
classMapper.updateClassName("特色一班",1);
sqlSession3.commit();
// 仍然从缓存中查出
System.out.println("studentMapper2读取数据: " + studentMapper2.getStudentByIdWithClassInfo(1));
}
执行结果
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.0
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: SELECT s.id,s.name,s.age,class.name as className FROM classroom c JOIN student s ON c.student_id = s.id JOIN class ON c.class_id = class.id WHERE s.id = ?;
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, name, age, className
TRACE [main] - <== Row: 1, 方方, 16, 特色一班
DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 1
studentMapper读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='特色一班'}
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.5
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='特色一班'}
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: UPDATE class SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 特色一班(String), 1(Integer)
DEBUG [main] - <== Updates: 1
DEBUG [main] - Cache Hit Ratio [mapper.StudentMapper]: 0.6666666666666666
studentMapper2读取数据: StudentEntity{
id=1, name='方方', age=16, className='特色一班'}
资源地址 https://github.com/zntzhang/mybatis-cache-demo.git
参考资料: